How to Calculate the Total Expenses From the Total Revenue and Owner’s Equity

It is important to keep in mind, though, that many accounting transactions don’t impact the owner’s equity. Let’s look at a couple examples of how owner’s equity can change for your business. By preparing an owner’s equity statement, businesses can effectively track and report changes in their equity, ensuring transparency and accuracy in their financial records. Conceptually, stockholders’ equity is useful as a means of judging the amount of money that a business has retained. Once you have this information, you can calculate it by subtracting the number of shares outstanding from the sum of the par value and market value per share. The asset equals the sum of all assets, i.e., cash, accounts receivable, prepaid expense, and inventory, i.e., $234,762 for 2014.

📆 Date: Aug 2-3, 2025🕛 Time: 8:30-11:30 AM EST📍 Venue: OnlineInstructor: Dheeraj Vaidya, CFA, FRM
Think of retained earnings as savings because it represents a cumulative total of profits that have been saved and put aside or retained for future use. Retained earnings grow larger over time as the company continues to reinvest a portion of its income. In addition, shareholder equity can represent the book value of a company. Equity can be found on a company’s balance sheet and is one of the most common pieces of data employed by analysts to assess a company’s financial health. On the other hand, shareholders’ equity consists of items such as common stock, preferred stock, additional paid-in capital (APIC), and treasury stock.
Retained Earnings (or Accumulated Deficit)
Another way of lowering owner’s equity is by taking a loan to purchase an asset for the business, which is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet. Although ROE examines how much profit a company can generate relative to its shareholders’ equity, return on invested capital (ROIC) takes that calculation a step further. Finally, negative net income and negative shareholders’ equity can create an artificially high ROE. However, if a company has a net loss or negative shareholders’ equity, calculating the ROE is not worthwhile. A good rule of thumb is to look for return on equity that is equal to or just above the average for the company’s sector—those in the same business.
- As always with financial statement ratios, they should be examined against the company’s history and its competitors’ histories.
- Most businesses use at least some debt to finance their operations, whether it’s a loan from a bank or a credit from the supplier.
- Boost your confidence and master accounting skills effortlessly with CFI’s expert-led courses!
- Mezzanine debt is a private loan, usually provided by a commercial bank or a mezzanine venture capital firm.
- Another way to boost ROE is to reduce the value of shareholders’ equity.
Can Owner’s Equity Be Negative?
Return on equity is considered a gauge of a corporation’s profitability and how efficiently it generates those profits. The higher the ROE, the more efficient a company’s management is at generating income and growth from its equity financing. In our modeling exercise, we’ll forecast the shareholders’ equity balance of contra asset account a hypothetical company for fiscal years 2021 and 2022. After the repurchase of the shares, ownership of the company’s equity returns to the issuer, which reduces the total outstanding share count (and net dilution). Also, you could calculate the revenue by multiplying the product units sold by the price of each unit. In this case, based on the total revenue figures on the income statement, Black Royal Inc. generated $4 million in total revenue by selling 20,000 outfits at $200 each.

Yes, this happens when a company finances more through debt than equity. While common in capital-intensive industries, excessive liabilities can signal financial risk. Understanding Owner’s Equity is crucial for investors, creditors, and the owner themselves to assess the financial stability and net worth of a business. It’s used in evaluating a company’s leverage, investment potential, and financial AI in Accounting health. Through years of advertising and the development of a customer base, a company’s brand can develop an inherent value. Some call this value “brand equity,” which measures the value of a brand relative to a generic or store-brand version of a product.
Understanding owner’s equity helps businesses track their financial health and is essential for decision-making. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity. It’s a core concept in modern accounting that provides the basis for keeping a company’s books balanced across a given accounting cycle. Shareholder equity can also be expressed as a company’s share capital and retained earnings less the value of treasury shares.
- Some of the reasons that may cause the amount of equity to change include a shift in the value of assets vis-a-vis the value of liabilities, share repurchase, and asset depreciation.
- We’ll learn how to do that step a little bit farther down in this post.
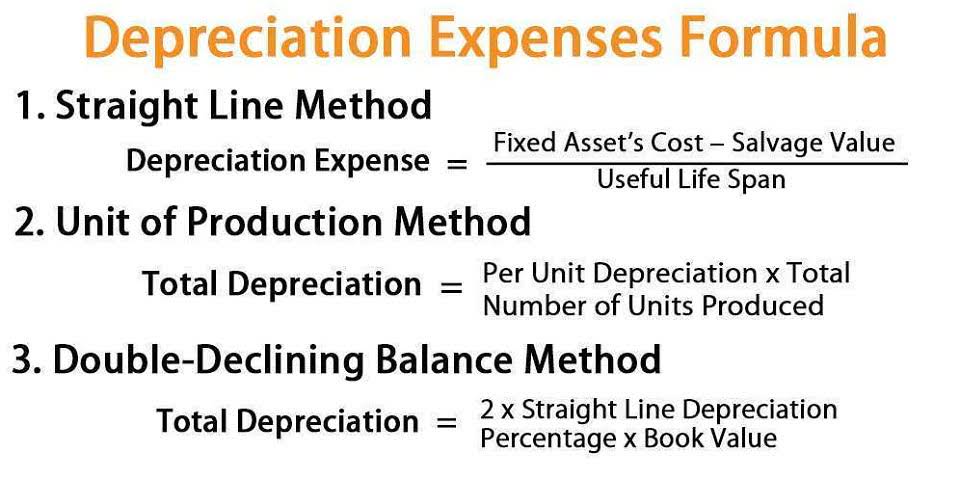
- They include the costs of buying raw materials, overhead costs, property taxes, leasing or mortgage costs and employee wages, among others.
- By analyzing how a company finances its assets, stakeholders can make informed decisions about investments, growth potential, and risks.
- The logic that underpins the owner’s equity formula is rooted in the fundamental accounting equation, , which states that total assets must equal to the sum of total liabilities and equity.
What Is Shareholders’ Equity in the Accounting Equation?
The value of the owner’s equity is increased when the owner or owners (in the case of a partnership) increase the amount of their capital contribution. Also, higher profits through increased sales or decreased expenses increase the amount of owner’s equity. Average shareholders’ equity is calculated by adding equity at the beginning of the period.
This concept is often used to evaluate a company’s financial standing and growth potential and calculate the return on investments. The owner’s equity may increase through business profits, new investments by the owner, or the retention of earnings. On the other hand, it may decrease due to losses, withdrawals by the owner, or how to calculate total owners equity debt payments.

